DC approximation¶
The so called direct current power flow (or just DC power flow) is a convenient oversimplification of the power flow procedure.
It assumes that in any branch the reactive part of the impedance is much larger than
the resistive part, hence the resistive part is neglected, and that all the voltages
modules are the nominal per unit values. This is, 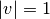 for load nodes and
for load nodes and
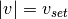 for the generator nodes, where $v_{set}$ is the generator set
point value.
for the generator nodes, where $v_{set}$ is the generator set
point value.
In order to compute the DC approximation we must perform a transformation. The slack
nodes are removed from the grid, and their influence is maintained by introducing
equivalent currents in all the nodes. The equivalent admittance matrix
(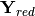 ) is obtained by removing the rows and columns corresponding
to the slack nodes. Likewise the removed elements conform the
(
) is obtained by removing the rows and columns corresponding
to the slack nodes. Likewise the removed elements conform the
(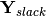 ) matrix.
) matrix.
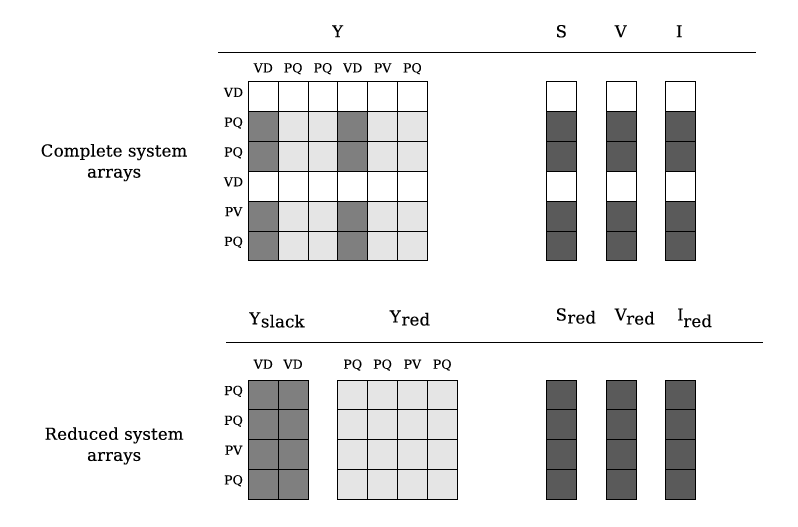
Matrix reduction (VD: Slack, PV: Voltage controlled, PQ: Power controlled)
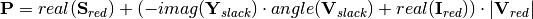
The previous equation computes the DC power injections as the sum of the different factors mentioned:
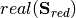 : Real part of the reduced power injections.
: Real part of the reduced power injections.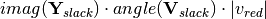 : Currents that appear by removing the slack nodes while keeping their influence, multiplied by the voltage module to obtain power.
: Currents that appear by removing the slack nodes while keeping their influence, multiplied by the voltage module to obtain power.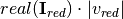 : Real part of the grid reduced current injections, multiplied by the voltage module to obtain power.
: Real part of the grid reduced current injections, multiplied by the voltage module to obtain power.
Once the power injections are computed, the new voltage angles are obtained by:
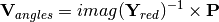
The new voltage is then:

This solution does usually produces a large power mismatch. That is to be expected because the method is an oversimplification with no iterative convergence criteria, just a straight forward set of operations.